The Future of Work and Why It Is Important to Embrace It
The future of work is looking past physically being there for work or at work.
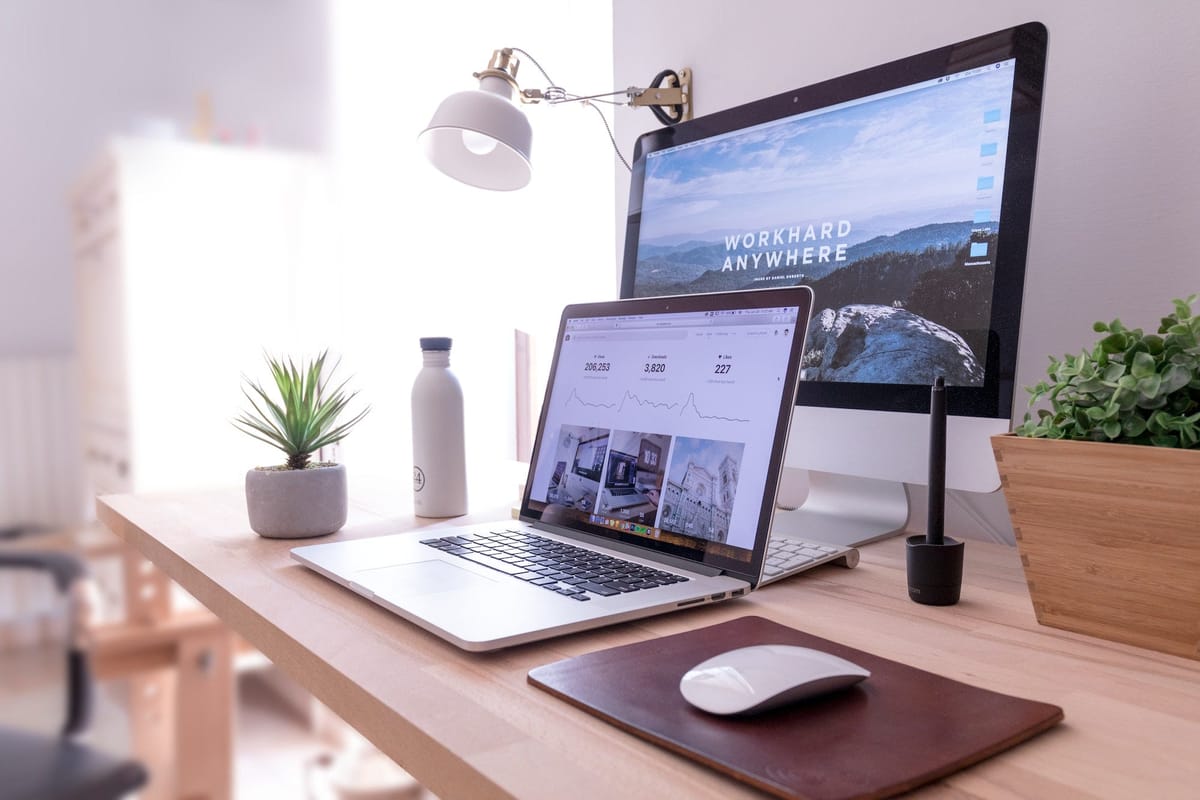

The future of work seems more uncertain today than it has ever been. In the years before, work was a physical thing and was appreciated as showing up somewhere, in person, and carrying out mandated tasks and responsibilities at the office or workplace. In such a setting, work was a daily event where every day needed planning and logistics to get yourself to work and to stay there for the allotted time. i.e., from 9 to 5.
The Cost of In-Person Work
Working in person comes with associated costs, and mostly these necessitate nearby accommodation, transportation, lunch money or at-work meals and beverages, and so on. It may seem benign, but in Cities such as Singapore, Hanoi, and Hong Kong, among many others, affording accommodation within the city or in the suburbs can be a tough call.
Gentrification and the Increasingly Unaffordable Cost of Living in Big Cities
The same goes for Amsterdam, New York, and elsewhere as gentrification, among other factors, has meant that the cost of living there is untenable. Such expense and the expensive nature of life in cities and towns globally mean that employment and physical jobs are difficult to source and sustain or even make enough to break even. If a major part of one’s income is spent on the facilitation of getting to work or sustaining the job, then it is not economically sensible to have such a job.
The Cost of Work in Self-Employment
For self-employed individuals, expenses could also mean rent, employee wages, tax, and shop setting, among others. The reprieve for self-employed individuals is that, once the individual has sourced enough startup capital, they can better sustain the business as they would be keeping a majority of the earnings.
Again, this may not be the case also as being an employer, or a self-employed individual could mean sourcing raw materials, paying staff, dealing with tax and regulatory requirements, bookkeeping, and compliance, among many others. These can be expensive and in most instances, starting out is the most challenging part of becoming self-employed.
The Increasing Risk Associated with Self-Unemployment Due to Limited Capital
Unfortunately, there is also increased risk in self-employment as the business could potentially crumble due to a lack of enough funds, global economic downturns, unfavorable regulations, and even low customer buy-in. The advantages that big companies have are that they have developed systems and relationships over time, and can rely on trusted partners and be relied on to deliver. Such facilitation or a head-start lacks for businesses that are just starting out.
The Need for Startups to 'Feed at the Bottom of the Tank'
Startups need to feed at the bottom of the tank in the meantime. i.e., develop relationships and partnerships with other small businesses. As smaller businesses grow, the startups will grow with them and eventually become big companies. Many of the work expenses relate to the need to be physically present somewhere on a job or to open up a physical shop as part of self-employment.
Reducing the Costs Associated with In-Person Work
The future of work is looking past physically being there for work or at work. The benefit of finding alternative ways to work is that it reduces the costs associated with working—for instance, rent, transport, at-work meals, etc. The benefit of such cost reduction is that both the business and its employees can save money by not necessarily showing up at work and working at home or telecommuting.
The Burgeoning Cost of Office Space
Even for big multinationals, renting or buying office space is not cheap, and the bigger the company, the more office space it needs, among other facilitations. When employees show up and work in an office, there is also the need to hire supervisors and managers. There are also costs related to cleaning, office supplies, and equipment, among others. All these make it more expensive to work physically or to run a business that has a physical store or location.
Virtual Work and Its Increasing Pervasiveness
The future of work stipulates that, where possible, employees and businesses can find non-physical or virtual ways to work and carry out tasks and responsibilities. The ability to undertake work virtually will most likely not be possible for all sectors and industries, as numerous sectors relied on human skills and functions.
Good examples include the medical field, specialist fields, sports, crafts, and many others. These are businesses, industries, sectors, and fields that necessitate employees or managers to be present in a physical location, doing physical work, or work that necessitates hands-on skills.
What is the Future of Work Like for Sectors that Cannot Automate
Restaurants and the catering sector, for instance, may not have the ability to go virtual as the services rendered necessitate human workers doing work with their hands. Even as robots and robotics have been seen to make, serve, or deliver food, there still needs to be human employees to fine-tune the services. As such, not all sectors can or would be incentivized to go virtual.
The Allure of Going Virtual for Companies that Can Automate
On the other hand, some sectors and fields can absolutely go virtual. Even with concerns about whether telecommuting could affect teamwork and collaboration, these are sectors that can go fully virtual. Excellent examples include the technology or tech sector where employees can work on their computers and not necessarily need to be physically present in an office.
Bolstering Online Security and Protecting Company Data and Information as Part of the Future of Work
Going virtual, however, necessitates adequate training and system security to ensure that even employees who are working at home can securely access, share, and distribute company information. The benefits and cost savings of telecommuting would otherwise be negated by a lack of adequate system security and the loss and unauthorized access to company information and secrets.
The Need for Intellectual proper Rights Considerations, Trademarking and Copyrighting in the Future of Work
The need for security for technological systems can also be tied to a need for intellectual property rights (IPR) considerations, trademarking, and copyrighting. As such, even when a company’s employees work remotely, the material they produce can be protected virtually, and also, as it is shared or distributed online.
Groupthink and its negative effects could be an unintended consequence of working physically. There is yet to be evidence of whether telecommuting has benefits in bolstering teamwork while reducing groupthink.
Investment in Technology and Why It is Crucial in Ensuring a Bright Future for Work
The future of work necessitates a lot of investment in systems and technologies to facilitate virtual work. An excellent example is the need for networking and communication systems and software, created by the current pandemic and ensuing lockdown.
The pandemic has shown technological systems’ potential and capabilities in connecting people and allowing for non-physical team member and business interactions. Today’s technology is not adequate for telecommuting, as even where systems are reliable, they need to be scaled and expanded to meet the growing need for telecommuting.
The Beauty of Technology that Allows for Remote Collaboration in Product Development
You can imagine programmers collaborating in making a console game, for instance, and needing to upload terabytes of data to conjoin their modules to create a single game. The same can be said for animation and movie directors, producers, and creators. There is a need for technology that can handle huge amounts of data instantaneously.
The Huge Role that 5G technology will Play in the Future of Work
A big part of doing this is ensuring adequate internet services and connectivity, including technologies such as 5G communication. 5G technology will be a major part of getting the world to a place where work can go virtual and be done at home or elsewhere, not necessarily in the office. Innovation will also be a key driver for the future of work.
The Skills and Training Needed in the Future of Work
The future of work will also necessitate training and learning in terms of how to work remotely. Such training will include technical training to ensure that employees can effectively use numerous technologies and perform virtual tasks. These include video conferencing, making digital presentations, communications, data sharing, and online security, among others.
The Importance of Training for the Future of Work
Training will ensure that employees can effectively carry out their roles remotely. There will also be the need to provide the needed technologies and devices to employees, including computers, phones, audio devices, etc. On the part of the employee, they will need adequate space in their homes for office space and an environment that promotes work and allows them to focus. As such, they can be in a position to spend time, as needed, to accomplish their tasks.
The Importance of Bolstering the Focus of Employees
When employees are too distracted to work remotely, then the company loses productivity and the speed at which work is done. As such, even telecommuting as a concept for work will necessitate companies to establish policies and procedures for working remotely. There will also be the need for performance measurement systems that transcend in-person supervision and employee observation. These will allow companies to rank their employees and grade their work effectively.
The Need for Effective Performance Measurement for Telecommuting
Effective performance measurement for telecommuting means that employers and managers will be in a position to promote employees who work remotely and develop managerial skills even on a virtual basis. The future of work is definitely virtual and as difficult and complex as it sounds; it is possible and could save numerous businesses from becoming too expensive to run.